Garbage Can Model Decision Making in Management Literature Review
Introduction:
Life is made upon the decisions. Individuals, regardless of their age, career, and whatsoever other cistron, brand decisions on virtually daily routine. Decisions may have modest or big scopes with short term or large term impacts on individuals or group of people. No one can deny the office of decisions, either made by him/herself or someone else, on his or her life.
Go Assistance With Your Essay
If y'all demand assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help!
Essay Writing Service
Similar to human being beings, organizations are dealing with the decisions that are made in them every single day. Although all the managers at whatsoever level, and even sometimes employees, make decisions, the of import decisions including strategic decisions are usually made by senior and tiptop managers across organizations. Based on the nature of decision and other factors, their lifetimes and their furnishings may vary. Strategic Decisions are amongst the most important ones that are made in whatsoever organization and usually accept long lasting effects on the companies. The importance of strategic decisions is undeniable, so it is worth exploring its procedure and any factor pertaining to it. In this course newspaper, I endeavor to review the existing literature on strategic conclusion making procedure.
Environmental factors and constraints shape the chief framework for managers, and most of the managerial decisions are inevitably influenced by internal and external ecology boundaries and constraints. (iv) The environment is e'er changing and the dynamic condition of global brings doubtfulness and risks into the managerial decision process. On the other mitt, due to time, knowledge and other limitations and restrictions, managers make decisions with uncertain and incomplete information. Some managers employ intuition to handle existing uncertainties and deal with organizational bug. According to the Klain, 90% of managerial decisions are fabricated intuitively (Klain, 2004).
Strategic Decision
For defining strategic decisions, it is better to start with definition of decisions in general. Based on the Meriam-Webster lexicon decisions are "conclusions or resolutions reached after consideration." Based on this basic definition, each conclusion has iii chief steps: First, identification of need or a dissatisfaction of current situation or; Second, moving towards satisfaction or filling the recognized demand; Tertiary, a conscious dedication to implement the deportment regarding reaching to the point of fulfillment (Arsham, 2010).(1)
Strategic decisions are the decisions that influence the long-term state of the arrangement. In general the procedure of developing and putting into activeness choices that lead to major organizational changes is chosen strategic decision making process. (ii) Strategic decisions commonly bring long-term financial and not-financial commitments to the organizations and it'due south usually hard to reverse the strategic decisions in one case they are implemented in the organizations. (2) Therefore, managers for making the strategic decisions, unlike mutual managerial decisions, use more time and try and pay more than attention (4). Strategic management involves with unplanned, unstructured and complex problems; thus strategic decisions are made nether uncertainty (Rutherford-Silvers J., 2008; Dragomir, C., 2012; Stefanescu, R., 2013).
The strategic decisions unremarkably play the bridge role betwixt current and future states of the organisation (Papadakis & Barwise, 1998). In add-on, the strategic decisions play the remarkable roles in organizational learning processes and managers should handle the evolving conflicts between practical and bookish disciplines in the strategic determination making process (Papadakis & Barwise, 1998).
In strategic decisions, managers try to harmonize organization capabilities and resources with the ecology opportunities and threats.(3) In other words, strategic decisions deal with environment and manufacture in which the organization operates; tangible and intangible resources which class the organization; and the connection and relationship between these ii groups at the same time (4).
Operational and administrative decisions are different from strategic decisions. Administrative decisions are system's routine decisions that facilitate execution of the operational decisions. Operational decisions are fabricated upon technical noesis of employees and facilitate execution of the strategic decisions. (3) For example, moving towards cost leadership strategy managers may reduce the number of workers which is an operational decision and it tin can be achieved by some administrative decisions. (iii)
Strategic Decision Making Models
The all-time and most effective strategic conclusion model may vary based on the organization situation, manager's personality, and some other factors.(four) For instance, if the output of the decision should exist implemented by group of people, its decision making procedure is totally dissimilar from the procedure of the decision which its output can be implemented just by the decider. (4)
There are ii main approaches in categorizing the strategic decision making models: i) based on the number of steps 2) based on the context and application. Both approaches take some similarities and they tin be combined together in some situations.
Models of decision-making based on the number of steps:
Series of new contributions on process of strategic decision making take been offered in concluding decade (Jalal-Karim, A., 2013; Verboncu, I., 2011; Nobrega, C.M. et al., 2009; Wildman, J.L. & Salas, E., 2009; Nooraie, M. 2008; Quintus, J.R. & George, J.M., 2005). Mostly, the strategic decision making process starts by recognizing an upshot or an opportunity. Although anyone in the organisation can find the problem or opportunity, generally top managers recognize them and try to accurately specify some alternatives to attack them. According to Cornescu, managers may face some obstacles in accurately defining the consequence that is the main subject of strategic determination: selective perception, but considering effects and not paying attention to causes, defining problems based on alternatives then on (Cornescu, 5. et al, 2004).
Strategic decision making models consist of the steps which guide the decider to reach better decisions in any situation. In the categorization of the decision making process based on the number of the steps, unlike authors and researchers defined dissimilar number of steps or stages: vii stride decision making process, 5 step conclusion making process, 4 stage decision making process or innovative determination making process, iii step conclusion making process and etc
Regardless of the decision making process, there is one step which is the aforementioned in all of these models: defining the trouble or the field of study of the decision to make. However, the primary feature that discerns the decision making and problem solving is related to the human's bounded rationality. In problem solving procedure, thinking and the heuristics play the most important roles, and the specific solution is generally captured at the end of the process. On the other side, in the conclusion making process, the decider cannot fully analyzes the state of affairs rationally and emotions cannot exist excluded from the procedure.
Anyhow, in many cases conclusion making and problems solving are replaceable terms and functions. In improver, since one of the chief stages of problem solving process is choosing an alternative to solve the problem, the problem solving can be recognized equally one blazon of decision making. And since in many cases the decisions are made nether time pressure, the process of decision making can be defined every bit i blazon of the trouble solving procedure. According to the mentioned reasons, many people consider decisions as problems to be solved and problems as decisions to be made. (4)
vii Step Decision Making Process
In this model, the process of decision making has seven steps and the entire model is divided into three chief stages which are defining the state of affairs, identifying, and developing the deportment (Figure i).
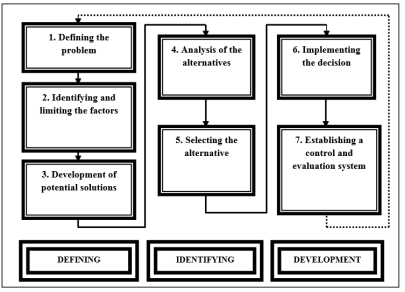
Lintherland identified 7 steps in decision making procedure:
1. Defining the trouble
2. Identifying and limiting the factors
iii. Development of potential solutions
4. Analysis of the alternatives
5. Selecting the alternative
6. Implementing the decision
7. Establishing a command and evaluation system (Lintherland, 2013)
This model of conclusion making process is used past most of the managers in real globe (Lintherland, 2013).
5 Pace Determination Making Procedure
Doyle introduced the 5 step decision making process model (Effigy 2) (Doyle, 2012). This model besides used in the real world and its stages are:
- Identifying conclusion
- Options examination
- Gathering data
- Making decision
- Implementing decision
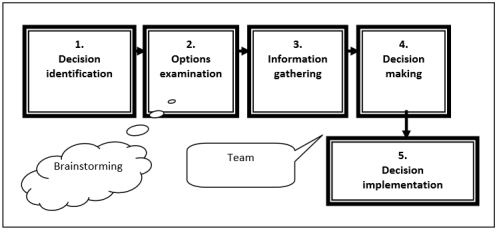
In this model, the first pace plays a remarkable part. The decider should write all factors and topics that may affect conclusion and form the decision in unlike ways till the determination precisely fits the decider's need and wish. In order to identify the conclusion accurately, the manager tin can use the answers to the questions like: What? When? Which? How? What if? and etc. (Doyle, J., 2012).
In 2nd footstep, "options examination", the decider should formulate the various scenarios and place the outputs of the unlike options and scenarios. In this stage, more information and assumptions effectually the subject of the determination are recognized. In order to shaping the framework more accurately and finding missing data, brainstorming with other employees is highly recommended to managers. (iv)
three Step Decision Making Process
Chestnut introduced a three stride decision making model, the stages of this model are: identification of need or opportunity, building decision components and implementation of decision (Figure 3).
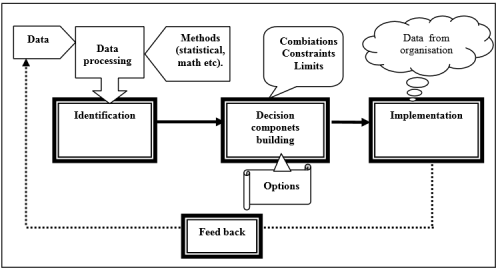
Figure three – three step conclusion making model
According to Chestnut, in the identification stage, managers capture internal data and utilise statistical and mathematical methods on gathered information and use the ouputs of the statistical methods to make a decision (Chestunt, D., 2013).
Second stage in this model is "edifice components" stage in which the decider considers all possible combinations of limitations and constrains into their models and assesses the effect of each possible selection. The final list includes all the possible decisions and the probabilities of their success rate.
The last stage in this model is implanting the decision. In this model, like the 5 step decision model, the support system in the organization plays an important role and it's crucial to track the outcomes continuously to modify the actions within the organisation.
3 Step Decision Making Procedure
Chestnut introduced a 3 step conclusion making model, the stages of this model are: identification of need or opportunity, building decision components and implementation of determination (Figure iii).

Figure 3 – 3 pace determination making model
According to Chestnut, in the identification stage, managers capture internal information and use statistical and mathematical methods on gathered information and employ the ouputs of the statistical methods to brand a conclusion (Chestunt, D., 2013).
2nd stage in this model is "building components" phase in which the decider considers all possible combinations of limitations and constrains into their models and assesses the effect of each possible pick. The final listing includes all the possible decisions and the probabilities of their success charge per unit.
The concluding stage in this model is implanting the decision. In this model, similar the 5 stride conclusion model, the support system in the organisation plays an important part and information technology'due south crucial to track the outcomes continuously to modify the actions inside the organization.
Strategic Decision Models Based on the Context and Application
There is another categorization for strategic decision models. In this categorization, the models are separated based on their chief characteristic, context or application (five). Some of the most well-known are introduced in this class paper:
- Rational Model
- Divisional-Rationality or Behavioral Model
- Bargaining Model
- Participative Model
- Garbage Tin Model
1. Rational Determination Making Model
This model, too known as "the rational comprehensive" model, is based upon the famous economic approach in which the ultimate goal of any action or change is maximizing the efficiency of specific criteria past choosing the all-time choice. This model is usually divided into 6 specific steps:
- Defining goals
- Recognizing alternatives
- Examining the consequences of each alternative
- Making conclusion based on the specific criteria
- Monitoring implementation
- Modifying the initial decision based on the feedback
This model is widely used past practitioners more often than not because of its attractiveness and simplicity. This model offers a structured approach to address outcome or opportunity and assistance managers reach the decision. This model overlooks any doubtfulness and information technology is all-time suited for well-structured and elementary problems in predictable industries. Based on its feature, the main application of this model is in technical environs where goals are accurately divers and there is an agreement on the criteria and measurement of goals. For instance, NASA uses the rational model since engineering factors, procedures, and goals are relatively clear and less ambiguous. This model is difficult to apply in the organizations which operate in dynamic and political environment. The issues and opportunities in the dynamic environment are complex, therefore the unmanageable number of possible options should exist considered before making decisions in this approach.
In addition, the existing complexity and uncertainty in the dynamic environments would also decrease the conviction of the decider in evaluating dissimilar alternatives.
2. Bounded-Rationality or Behavioral Model
Herbert Simon, Nobel Laureate, criticized the rational decision making approach and introduced the concept of "bounded rationality" (five-4). Co-ordinate to this concept:
- Humans cannot make fully rational decisions mainly because they can process and consider a little amount of data at the moment.
- Expertise, information, and time in each state of affairs are limited; therefore the comprehensive assay is very difficult and almost impossible in most cases.
- Humans tin not consider and recognize all possible limitations and constraints of an event, thus not all of the possible alternatives are analyzed in the rational decision making procedure.
In real world, because the rational limitations the managers unremarkably simplify the trouble and restrict themselves to simply several principal options. Decision makers usually identify a few numbers of criteria and commonly assess the options that have worked for their organization or other similar companies before. Dissimilar the rational model, the behavioral model does non address only 1 best solution for a problem. The advocates of this theory believe that managers based on the factors such every bit managers' characteristics, organization'due south state of affairs, and other factors tin can find various solutions for their issues. Simon asserted that since all the information is not available for a decider, the managers who use the bounded-rationality model, different rational model, seek "satisfaction" for their problems and not "maximization". (Simon) In other words, this model shows a decider the "adept enough" options to meet minimum selected criteria at the determination making time. In this model, the "criteria weighting" plays an important role in making ultimate decision.
iii. Bargaining Model
The main application of this model is in the situations where two or more parties engaging in the decision may have disharmonize of interest. The representatives of the organizations should larn and know the principles of negotiation. Senior managers select this approach in the strategic decisions which involve tradeoff between different organizations or between unlike parties within the organization. In this model, the managers or negotiators seek the common benefits or common interests to maximize the adventure of reaching to the appropriate conclusion. The resulting decision should be adequate by all the involved sides.
Notice Out How UKEssays.com Tin can Aid You!
Our academic experts are set and waiting to assistance with any writing project you may take. From simple essay plans, through to full dissertations, yous tin can guarantee we have a service perfectly matched to your needs.
View our services
The bargaining model is highly used in politics mainly considering in this context many agile parties are fed from the aforementioned fiscal and non-financial resources and these resources are limited. Yet, some argue that using bargaining model in politics can pb to distribute power as that consequently decrease the effect of power which is sometimes essential in the society, organization, and other communities. The bargaining model is useful for getting multiple views before making decision; and it can help managers make the more sustainable determination.
The bargaining model gives each party involving in the decision a position for reflecting their interests. Bargaining model pays a groovy deal of attention to the competitors and their actions in decision making process. One of the disadvantageous of this model is its time consuming feature in some cases since parties try to resolve disagreements. Although the interests of all parties are relatively considered in the negotiations, the wishes of the most powerful sides are more than likely to be met than needs and wishes of the least powerful parties. In practice, some managers exclude some parties from bargaining model for getting agreements more quickly and saving time, but this approach threatens the success of the resulted decision since some parties may non support the actions pertaining to the decision. To sum it up, the larger puddle of participants in bargaining decision making model leads to ameliorate notwithstanding more time consuming decisions.
iv. Participative Decision Making Model
The bargaining conclusion making model is expanded and formed the participative decision making model. The participative conclusion making model tries to bring all the people who straight influenced by the conclusion into decision making process. This model is known as the most democratic decision making process. Still, the participation of people in the process of decision making in this model plays just the "consultation" function and non "deciding" role. In other words, this model provides people the opportunities to bring ideas and information to the tabular array simply they do not have real decision making ability. Whatsoever stakeholder group inside the organization may accept its own agenda and interests to pursue; therefore in this model, the stakeholders are encouraged to present their key concerns before decisions are made. It is worth mentioning that stakeholder groups are sometimes strong enough to hinder the process of determination making if they are not included in the process of decision making. Participative decision making model tin be seen in NATO, Un, and other global bodies.
The major disadvantages of participative conclusion making model are its expensiveness and slowness. Information in this decision making model act equally double-edged sword, while the information from different perspectives can clarify various aspects of the issue, the huge corporeality of unstructured information is somehow a problem for managers. For having successful participative decision model, participants should try to subordinate their own interests in pursuit of common objectives.
5. Garbage Can Model
According to Cohen, March, and Olsen, many decisions are fabricated based on unorganized interactions of agents and opportunities, chance, and the current available human skills and other resources within the organization. (25) This model implies that organizations and managers take dynamic, sick-divers, and inconsistent preferences, and organizations are run on a basis of trial and mistake. Stakeholders partially understand the processes in the organization, and the deciders act randomly and impulsively. Based on the illustrated framework, Cohen et al. argued that managers inside the organizations retrieve of many solutions when they have not faced bug still. They keep these solutions and utilise them when the problems occur within the organisation. They asserted that: "decisions are dumped in a holding tin – the garbage can for hereafter use." (Refr)
Managers employ garbage tin model in highly ambiguous environments which called structured anarchies. Cohen et al. argued that deciders are every bit probable to place their goals through actions equally they are to find them prior to decision. In add-on, they argued that due to existing organized anarchies within the arrangement some technologies used in the organizations are unclear. Moreover, they argued that managers have loose understanding of goals and ways at the first. Cohen et al. fence that organizational participants learn through trial and error actions without understanding the causes. They also argued that in near cases the decision making participants come and go into the process constantly and their involvement vary considering of their involvement, energy, and fourth dimension (Cohen et al., 1972). Thus, it'due south very hard to recognize who will really participate in a decision (Cohen et al., 1972). The garbage can model introduces four streams of randomness: one) randomness in opportunities 2) solutions iii) participants iv) problems. Therefore, the conclusion making procedure is full of randomness and the resulted decision can be selected randomly. Summarily, Cohen and his colleagues argued that decisions are not the outcome of rational analysis or coalition of powers but rather random events. On the other hand, some scholars contend that garbage tin can model does not offer a theoretical framework and this is its principal disadvantageous and cannot exist widely used in real world.
In improver to the mentioned decision making models, the researchers introduced some other models that such as incremental and polis models.
depasqualecuses1966.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/business/types-strategic-decision-models-3462.php
0 Response to "Garbage Can Model Decision Making in Management Literature Review"
Post a Comment